Postgraduate Debt Remains a Concern for African American Students
Even with UA scholarships designated for minority students, some African American take out federal loans to cover the cost.
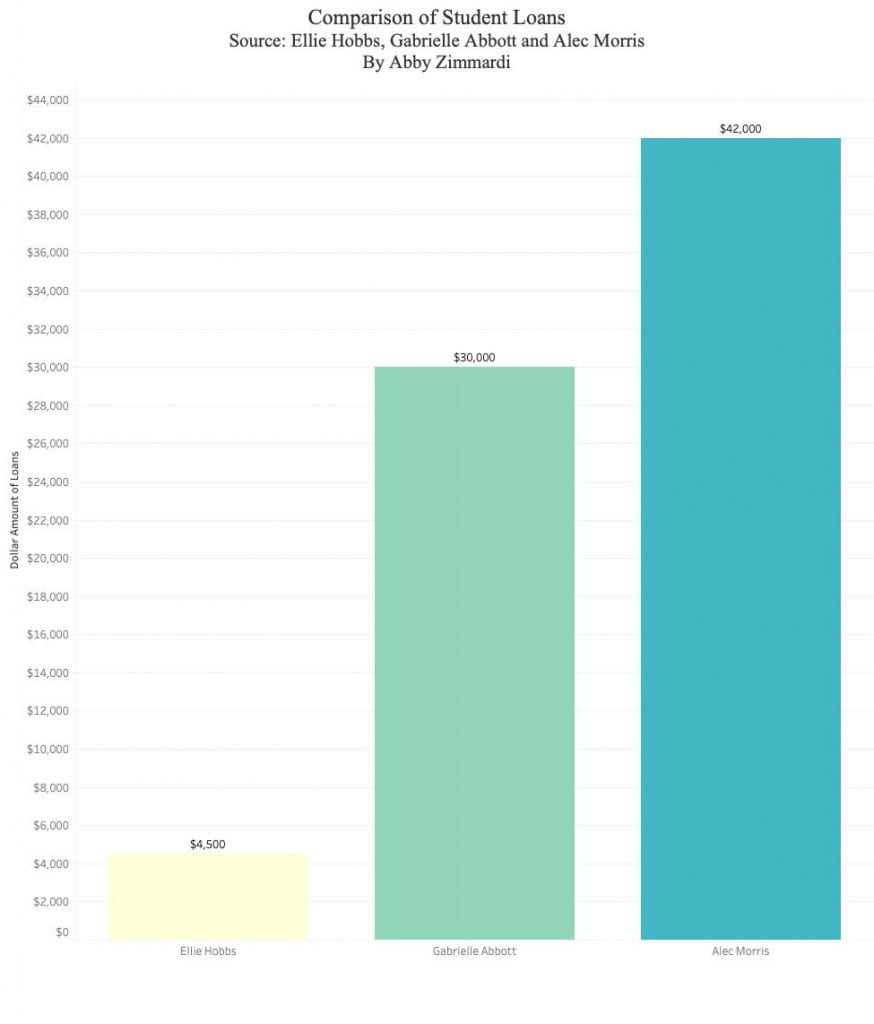
By Hanna Ellington
The Razorback Reporter
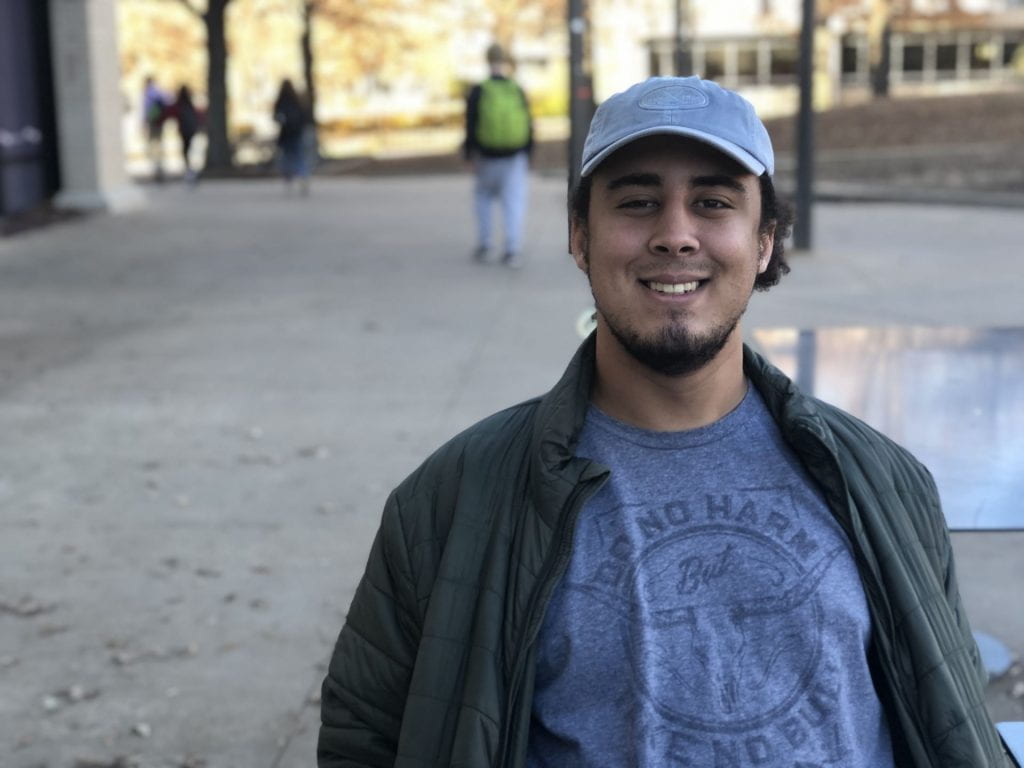
Dylan Williams grew up in a military family, and he is preparing to follow in his father’s footsteps by joining the U.S. Army, in part to help cover the financial burden of college.
Williams, set to graduate from the UofA in 2021, said joining the Army offers the potential benefit of cancelling the student debt he acquired in college.
“There’s a pretty hefty signing bonus, especially for the occupations that I’m looking at specifically in the Army,” Williams said. “When you reach a certain point in your military career, they have loan repayment programs that will allow you to have the government pay back your debt from school.”

The University of Arkansas offers three scholarships specifically for students from underrepresented areas, which includes minority students. But, African-American students such as Williams still borrow more than other students, according to the U.S. Department of Education.
In Arkansas, African-American students borrow on average $14,694, nearly $3,000 more than white students’ average of $10,827, according to a 2015-16 study by the Department of Education. African-American students have the highest borrowing rate across the country with an average of 88% of students taking out loans, according to a 2015-16 Education Department study.
When taking out loans, some students don’t consider the future repercussions because of the need for money in the present, Williams said.
“I need this money now, and what am I supposed to do without it? I’m not looking at paying it back now,” Williams said.
Williams, 20, a public health major from Conway, received the Silas Hunt Scholarship, one of the three scholarships given to excellent students from underrepresented communities. “It was a pretty big help for me,” Williams said. He credits the U of A with “trying to do something about that problem by offering these scholarship opportunities for minorities, so they’re not faced with the cycle of not being able to afford college.”
Other scholarships in this category include the Razorback Bridge and the University Enrichment scholarships. All three of these scholarships can total up to $48,000 for all four years, according to the UA scholarship website.
“This allows a broader section of the population from Arkansas to attend the university,” said Denise Burford, associate director of financial aid. “Anytime a student gets a scholarship, they’re more likely to attend. It shows interest in the student.”

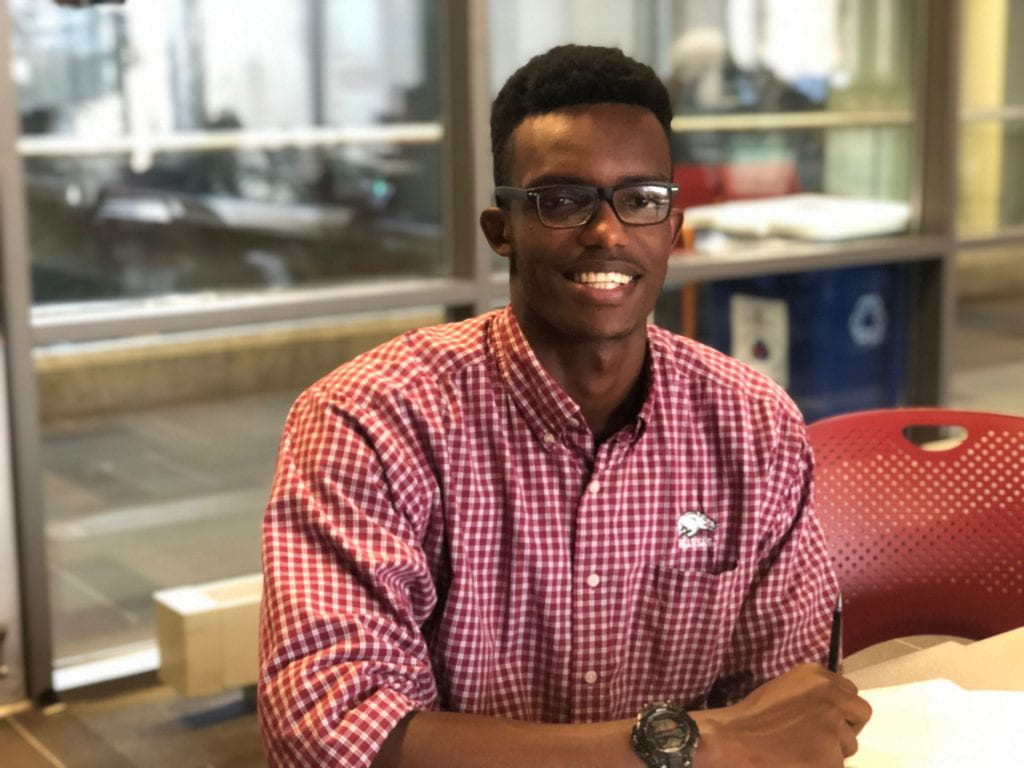
For Yves Manzi, 20, a civil engineering major from Rwanda, scholarships were a defining reason for attending the UofA, he said. In addition to assistance from his parents, Manzi supports himself through being a research assistant for the Engineering Department.
“Some of the college students that come here, maybe their parents can afford to pay half of it or something like that,” Manzi said. “But, most of the black students that come here, most of their parents don’t have the money to support half of the debt that they get.”

The average household income for black families was $38,731 in 2017, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. White families earned $14,000 more in 2017, with an average income of $52,768.
Minority students make up 20.5% of students at the UofA, with black students making up 4.4% of the student body, according to the Office of Institutional Research and Assessment. Only three scholarships are offered specifically to them.
The UofA is working to assist students by educating them about loans, Burford said. One of the ways is financial counseling through the Office of Financial Aid.
“We try to give options other than borrowing and explain the long term implications of borrowing,” Burford said.
Educating students on their college financing options could help students be more prepared, Williams said.
“I was lucky enough to have a college prep class in high school, and one of the assignments we had was to pick three colleges that we were planning on going to and then figure out the cost of attendance for a school year. I knew how much it would cost coming up here before freshman year,” Williams said. “In terms of finding out how the loans work, that was on me to figure out.”
In addition to his class, Williams’ father also taught him about loans. Williams is also receiving benefits, like an additional scholarship, from his father’s former employment in the military.
While Williams is certain on his choice to enter the military after leaving the UofA, Manzi is worried about the job prospects following graduation. The possibility of not getting hired because of one’s race is a concern for some students, Manzi said.
“I’m not saying that all companies are like this, but sometimes it’s hard to get a job when you’re a black student,” he said.
Since 2014, Arkansas men aged 18 to 24 have had the highest rate of poverty for men, with nearly 32,000 men living in poverty in 2017, according to the U.S. Census Bureau.